Explanation of Each Part
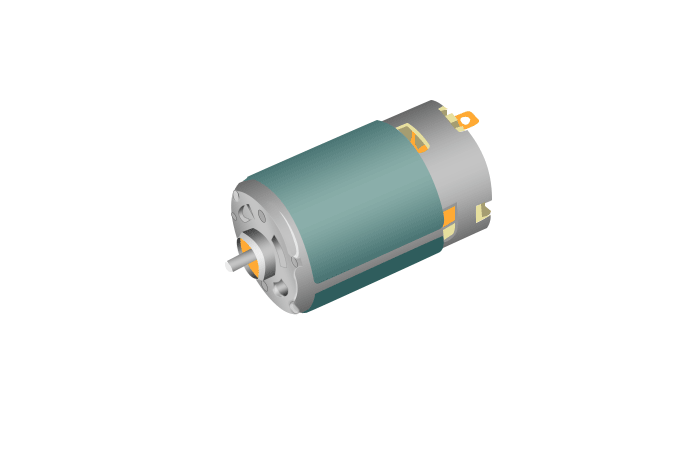
- Completed motor
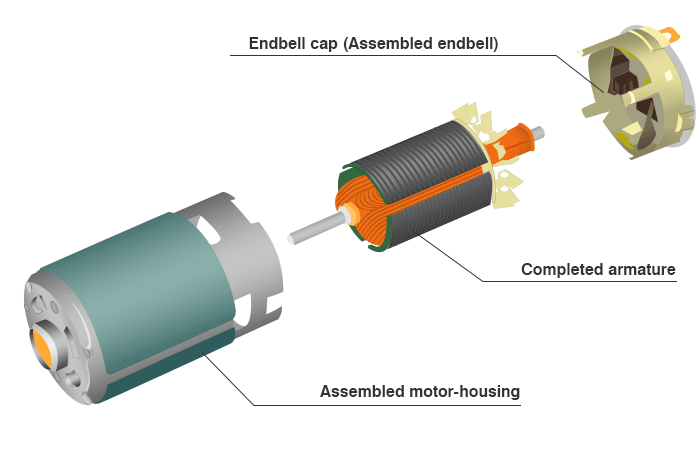
- Exploded diagram of completed motor
- Exploded diagram of motor-housing
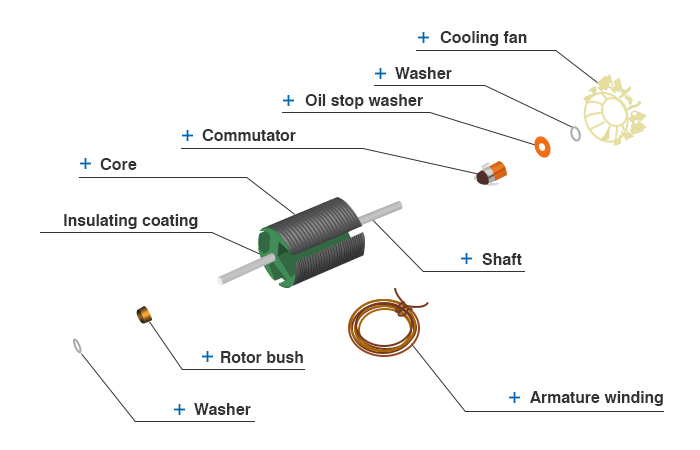
- Exploded diagram of armature
- Exploded diagram of endbell cap
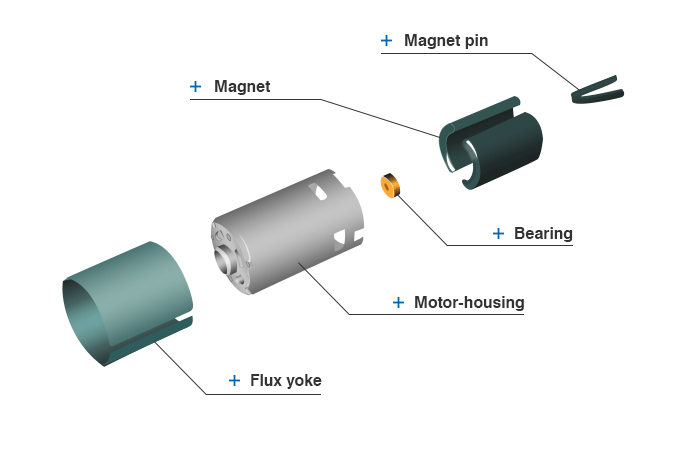
Magnet pin
An elastic pin to fix the magnet to the motor-housing.

Bearing
A part to support the shaft of the completed armature, mostly made by sintering metal powder. Contains innumerable oil holes that impregnate lubricating oil to make oil films between a shaft and itself. Called oilless metal, also.
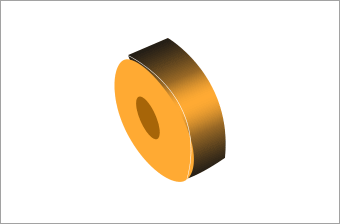
Magnet
A permanent magnet to produce magnet field that is the base to produce torque, turning force of the motor.
Flux yoke
An auxiliary steel sheet wound around the motor-housing, used for the motor with strong magnetic force to reduce the magnetic flux leakage from the motor-housing.
Motor-housing
A case used to fix magnets, bearings, and an endbell cap, constructs a magnetic circuit (magnetic field) with the magnets as a path for magnetic force to flow.
Cooling fan
A part that provides the current of air to cool the motor.
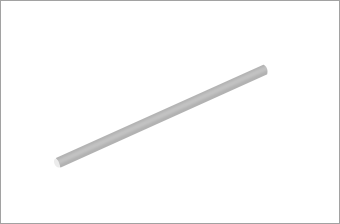
Shaft
Used to support the completed armature at the bearing. Output torque is transmitted through the shaft from the user's view.
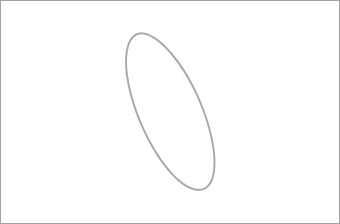
Washer
A fine adjustment part to adjust the endplay.
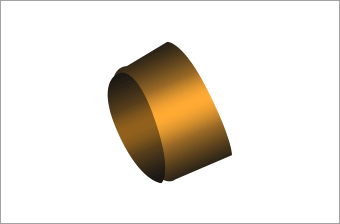
Rotor bush
A ring fixed to the shaft, restrains the movement of the completed armature in thrust direction to secure appropriate clearance (endplay).
Core
A path that enables electromagnetic force produced by current that flows to the coil of the completed armature to flow efficiently. Laminated cores are called core-shaft.
Armature winding
Armature winding determinates the electrical characteristics of the motor (by change of cross section and number of turns of winding etc.). However, some winding specifications are not available to produce though possible in theory.

Commutator
A point of contact that enables current conducted through the brush to flow to the armature winding in exact timing.

Oil stop washer
A washer that prevents the lubricating oil from flowing into the electrical contact portions, such as commutator and carbon.

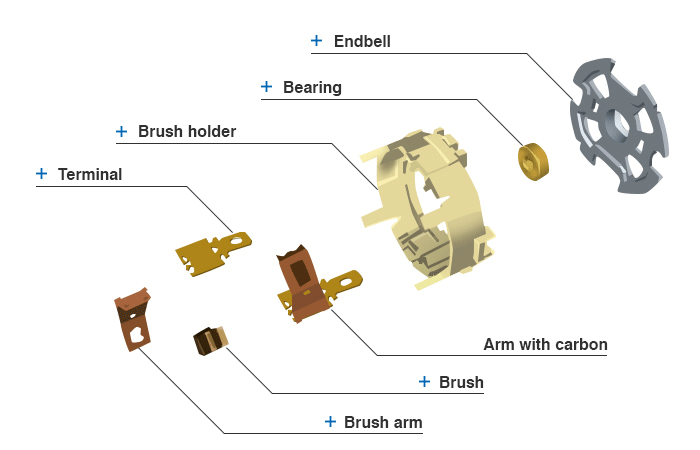
Endbell
A steel sheet that holds the bearing and that reinforces the brush-holder strength.
Bearing
A part to support the shaft of the completed armature, mostly made by sintering metal powder. Contains innumerable oil holes that impregnate lubricating oil to make oil films between a shaft and itself. Called oiless metal, also.
Brush holder
A part that holds the brush and that insulates it from the motor-housing etc. electrically.
Terminal
An external part of the endbell cap, provides the motor current.
Brush
A part that enables current to flow to the armature winding of the completed armature by sliding contact with the commutator. Mainly, a carbon is used at the sliding portion with the motor of high current, a special alloy plate of precious metal etc. with the motor of low current.
Brush arm
A part that supports the carbon brush and that enables the brush to do sliding contact with the commutator in appropriate pressure.
